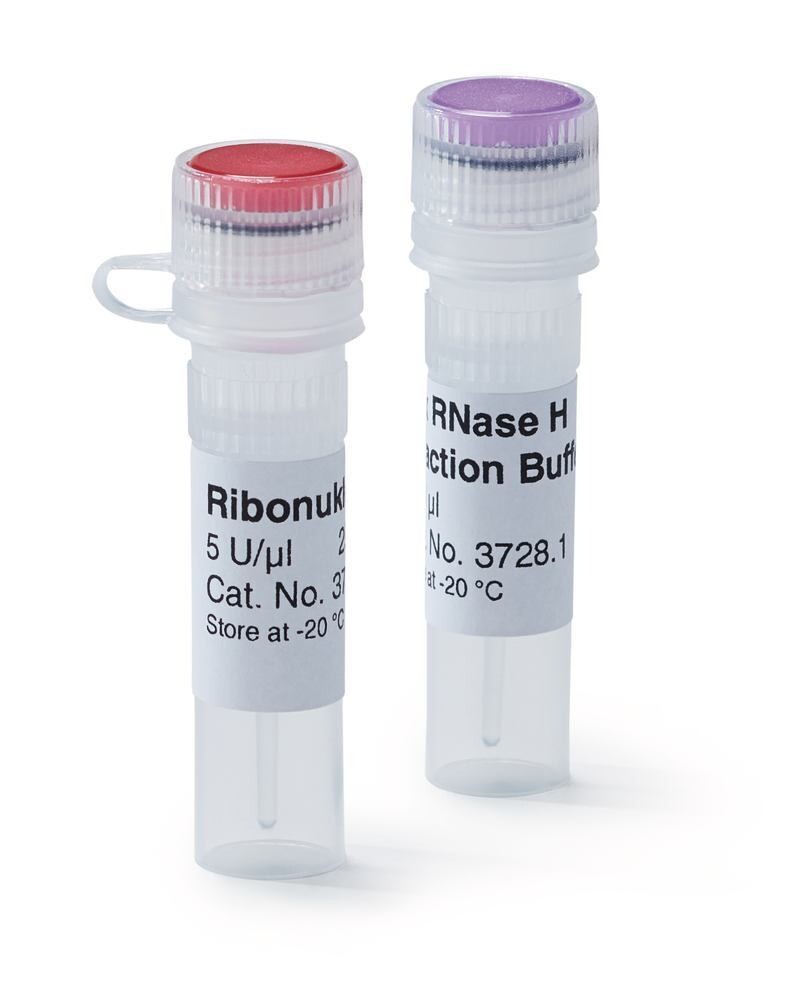
Ribonucléase H, 50 µl
Ribonuclease H 5 U/µl, for molecular biology
Non-specific endoribonuclease that specifically cleaves RNA into RNA:DNA hybrids. At least four continuous base pairs (RNA:DNA) are required for activity. The RNAse H cleaves RNA to release 5' oligoribonucleotides.
RNAse H does not degrade single and double-stranded DNA or unhybridized RNA.
RNAse H
Reaction buffer (10x)
The individual components of this kit cannot be purchased separately.
The kit consists of colour coded tubes for easy identification of the reagents.
Enzyme: a neoclassical, Greek artificial word ενζυμου, énzymon, derived from εν-, en- (in-) and ζυμη, zýmé (yeast, sourdough, archaic)
Ferments: comes from the Latin fermentum (ferments, sourdough)
There are six classes in which all enzymes are classified according to the particular reaction they catalyse:
• Oxidoreductases (catalyse redox reactions)
• Transferases (transfer functional groups among substrates)
• Hydrolases (cleave bonds via addition of water)
• Lyases/Synthases (cleave or synthesise complex products out of basic substrates without cleavage of ATP)
• Isomerases (transform chemical isomers)
• Ligases/Synthetases (cleave or synthesise complex products out of basic substrates via cleavage of ATP)
| Purity | ≥90 % |
| Concentration | 5 U/µl |
| DNases (exo-and endonucleases) | no |