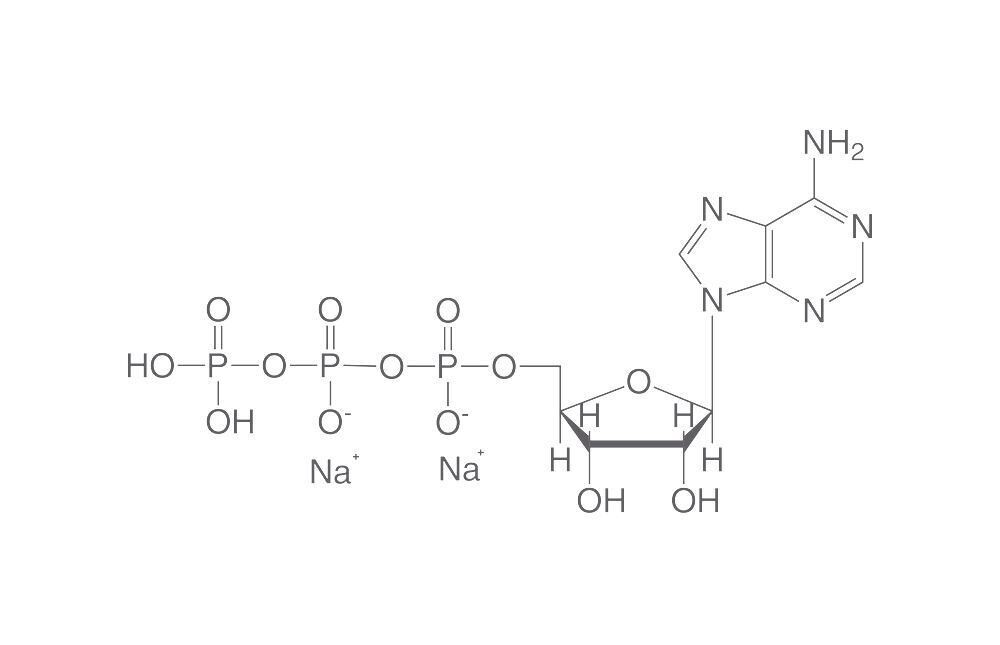
Sal disódica de adenosina-5-trifosfato (ATP), 5 g
REF HN35.1
€ 32,79
Disponible
1
Guardar este producto para más tarde
Sal disódica de adenosina-5-trifosfato (ATP), 5 g
Información del producto
Número CAS: 1400-62-0
Código hs: 29349990
Marca: Carl Roth
Adenosin-5'-triphosphate disodium salt, (ATP), min. 98 %, for biochemistry, Molar mass (M) 551,10 g/mol, Storage temp. -20 °C, CAS No. [987-65-5], EG-Nr. 213-579-1, Empirical formula C10H14N5Na2O13P3
Adenosin-5'-triphosphate disodium salt (ATP) ≥98 %, for biochemistry
Discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann. Main molecular currency of energy in all cells and highly important regulator of energy providing processes. During hydrolysis of phospho-anhydride bonds, energy of 30.5 kJ/mol (ADP) or 45.6 kJ/Mol (AMP), respectively, is released. Ligand of purinergic receptors and intercellular signalling molecule. Additionally, ATP is coenzyme of phosphate-transferring kinases like proteine kinases A, proteine kinases C, calmodulin-dependent kinases, and substrate of adenylate cyclases, which synthesize the second-messenger molecule cAMP.
| Assay (HPLC, dry substance) | ≥98 % |
| pH value | 2,5-3,5 |
| Chloride (Cl) | ≤0,05 % |
| Heavy metals | ≤0,002 % |
| Arsenic (As) | ≤0,0001 % |
| Loss on drying | 6,0-12,0 % |
Productos relacionados
Mostrar precios en:EUR
![(6-Phenyldibenzo[b,d]furan-4-yl)boronic acid, 97%, 5g (6-Phenyldibenzo[b,d]furan-4-yl)boronic acid, 97%, 5g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4763175074.png)

![7-Chloro-3H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyridine, 95.0%, 1g 7-Chloro-3H-[1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-b]pyridine, 95.0%, 1g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4782669547.png)



![METHYL 6-CHLORO-3-METHYLBENZO[B]THIOPHENE-2-CARBOXYLATE, 95.0%, 5g METHYL 6-CHLORO-3-METHYLBENZO[B]THIOPHENE-2-CARBOXYLATE, 95.0%, 5g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4780701542.png)
![(2E)-3-{4-[(2-chlorobenzyl)oxy]phenyl}acrylic acid, 95.0%, 1g (2E)-3-{4-[(2-chlorobenzyl)oxy]phenyl}acrylic acid, 95.0%, 1g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4763003073.png)

![7-Chloro-5-methoxy-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridine, 98%, 100mg 7-Chloro-5-methoxy-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]pyridine, 98%, 100mg](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4782663815.png)

