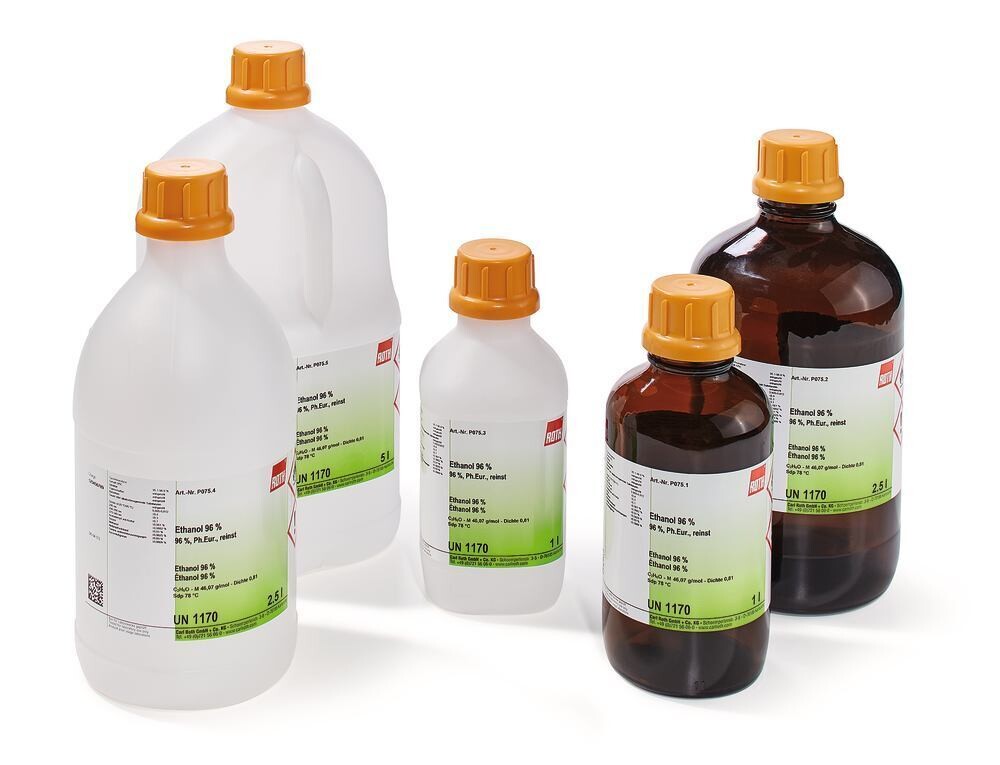
Ethanol, 2.5 l, plastic
Ethanol 96 %, Ph. Eur., extra pure
| Getest volgens artsenijboek | Ph. Eur. |
Acid Value Determination
The acid number characterises the acidic components of the fats. For this purpose, the sample is dissolved in a solvent and titrated against phenolphthalein with potassium hydroxide solution. Only free fatty acids are recorded. The fatty acids bound in the glycerides are not determined.
The saponification value denotes the amount of potassium hydroxide required to neutralise free fatty acids and saponify bound fatty acids. The lower the average molar mass of the fat, the higher the saponification value. The sample is heated under reflux in a defined quantity of ethanolic potassium hydroxide solution and the non-used alkaline solution is titrated with hydrochloric acid.
Hydroxyl Value
The hydroxyl value is a measure of the hydroxy group content of organic materials such as paints, resins, polystyrenes, solvents and lipids. It represents the amount in milligrams of potassium hydroxide required to neutralise the quantity of acetic acid that combines on acetylation of one gram of the substance being tested.
| Assay (V/V) | 95,1-96,9 % |
| Properties | complies |
| Identity | complies |
| Appearance | complies |
| Acid or alkaline react. substances | complies |
| Density (d 20 °C/20 °C) | 0,805-0,812 |
| Absorbance | |
| 240 nm | ≤0,4 |
| 250-260 nm | ≤0,3 |
| 270-340 nm | ≤0,1 |
| Volatile impurities | |
| Acetaldehyde and acetal | ≤0,001 % |
| Benzene | ≤0,0002 % |
| Methanol | ≤0,01 % |
| Evaporation residue | ≤0,0025 % |
| Sum of other impurities | ≤0,03 % |
| Volatile impurities | |
| Disregard limit | ≤0,0009 % |
| Prices include german tax on alcohol. | |



![TRANS-TERT-BUTYL HEXAHYDROPYRROLO[3,4-C]PYRROLE-2(1H)-CARBOXYLATE, 95.0%, 250mg TRANS-TERT-BUTYL HEXAHYDROPYRROLO[3,4-C]PYRROLE-2(1H)-CARBOXYLATE, 95.0%, 250mg](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4771361047.png)

![n-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]pyridine-2-carboxamide, 97%, 250mg n-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl]pyridine-2-carboxamide, 97%, 250mg](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4780577667.png)