D(+)-Saccharose, 1 kg
D(+)-Saccharose ≥99,5 %, RNAse/DNAse free
Sucrose gradient centrifugation has proven very effective in structural and functional analysis of macromolecular complexes. The distribution of macromolecules in gradients can be measured by UV absorption (A254).
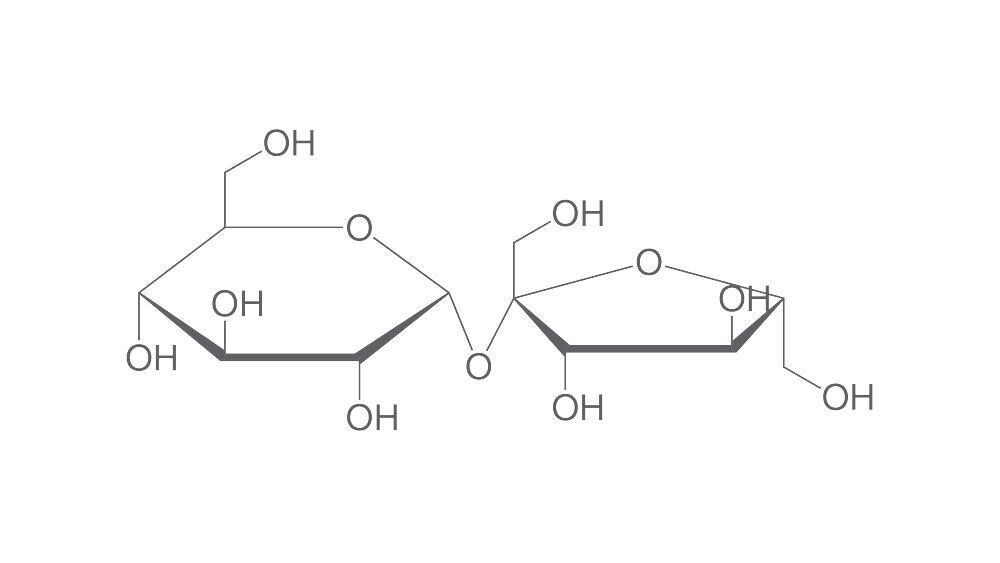
Carbohydrates or Saccharides make up 50 % of the dry biomass of the earth and are therefore the most frequent class of biomolecules. Besides at least two hydroxy groups, they also have an aldehyde or a ketone group and can be subdivided according to the number of monomeric components in mono-, di-, oligo and polysaccharides.
Whereas mono-, di- and oligosaccharides are soluble in water, taste sweet and are therefore called as sugar, polysaccharides are hardly, or not at all, soluble in water and have a neutral taste.
Carbohydrates, together with fats and proteins make up a large percentage of nutrition. In addition to their central role as an energy source, they are also an important structural component especially in plants (e.g. Cellulose). Ribose, a monosaccaride with five carbons (C5H10O5) is an essential element of coenzymes (such as ATP, FAD and NAD) and a structural component of RNA. Desoxyribose (a ribose derivative) is a structural component of DNA.
Disaccharides
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide units. These are interlinked covalently via a glycocide bond. The most familiar representatives are saccharose, lactose and maltose.
| Assay | ≥99,5 % |
| Endotoxins | <5,0 I.E./g |
| DNase, RNase | not detectable |
| Identity | complies |
| Conductivity | ≤35 µS/cm |
| Specific rotation [α]20D (c=26 in H2O) | +66,3 to+67,0 ° |
| Reducing sugar | complies |
| Invert sugar | ≤0,06 % |
| Sulfite (as SO2) | complies |
| Calcium (Ca) | ≤0,01 % |
| Lead (Pb) | ≤0.0001 % |

![(4'-Methyl-[2,2'-bipyridin]-4-yl)methanol, 95.0%, 1g (4'-Methyl-[2,2'-bipyridin]-4-yl)methanol, 95.0%, 1g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4763067337.png)



![trans-4-[Bis(phenylmethyl)amino]cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, 97%, 100mg trans-4-[Bis(phenylmethyl)amino]cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, 97%, 100mg](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4771359113.png)




