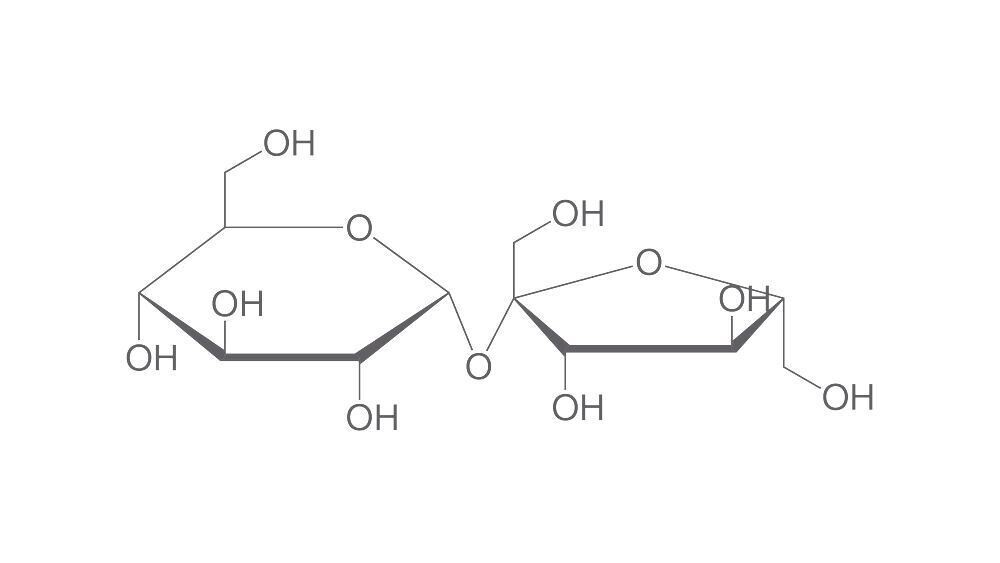
D(+)-Saccharose, 10 kg
Carbohydrates or Saccharides make up 50 % of the dry biomass of the earth and are therefore the most frequent class of biomolecules. Besides at least two hydroxy groups, they also have an aldehyde or a ketone group and can be subdivided according to the number of monomeric components in mono-, di-, oligo and polysaccharides.
Whereas mono-, di- and oligosaccharides are soluble in water, taste sweet and are therefore called as sugar, polysaccharides are hardly, or not at all, soluble in water and have a neutral taste.
Carbohydrates, together with fats and proteins make up a large percentage of nutrition. In addition to their central role as an energy source, they are also an important structural component especially in plants (e.g. Cellulose). Ribose, a monosaccaride with five carbons (C5H10O5) is an essential element of coenzymes (such as ATP, FAD and NAD) and a structural component of RNA. Desoxyribose (a ribose derivative) is a structural component of DNA.
Disaccharides
Disaccharides consist of two monosaccharide units. These are interlinked covalently via a glycocide bond. The most familiar representatives are saccharose, lactose and maltose.
| Assay | ≥99,5 % |
| Invert sugar | ≤0,04 % |
| Loss on drying | ≤0,1 % |
| Sulfite (as SO2) | ≤0,001 % |
| Chloride (Cl) | ≤0,002 % |
| Arsenic (As) | ≤0,00001 % |
| Lead (Pb) | ≤0,00005 % |
| Cadmium (Cd) | ≤0,00001 % |
| Chromium (Cr) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Calcium (Ca) | ≤0,001 % |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Potassium (K) | ≤0,005 % |
| Cobalt (Co) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Magnesium (Mg) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Manganese (Mn) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Sodium (Na) | ≤0,005 % |
| Nickel (Ni) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Mercury (Hg) | ≤0,000005 % |
| Zinc (Zn) | ≤0,0005 % |




![Benzo[b]thiophen-4-ol, 95.0%, 1g Benzo[b]thiophen-4-ol, 95.0%, 1g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4763350667.png)